About the Business Solution
- AllegroGraph is a Multi-model (Document and Graph) database technology that enables businesses to extract sophisticated decision insights and predictive analytics from their highly complex, distributed data that can’t be answered with conventional databases.
- Unlike traditional relational databases or more recently developed NoSQL databases, Franz’s product AllegroGraph employs a combination of document (JSON and JSON-LD) and graph technologies that process data with contextual and conceptual intelligence. AllegroGraph is able to run queries of unprecedented complexity to support predictive analytics that help companies
make better, real-time decisions.
About the Technology
- The AllegroGraph database is a modern, high-performance, persistent, semantic graph and document database. AllegroGraph uses efficient memory management in combination with disk-based storage, enabling it to scale to billions of triples/quads/documents while maintaining superior performance. AllegroGraph is W3C/ISO standards compliant and supports JSON, JSON-LD, SPARQL 1.1, RDFS++, SHACL, and Prolog rules and reasoning directly and from numerous client applications.
-
Key Features
- Multi-model Document (JSON, JSON-LD) and Graph Database (RDF, OWL)
- AllegroGraph is 100 percent ACID, supporting Transactions: Commit, Rollback, and Checkpointing.
- Industry’s most secure Graph Database with Triple Attributes.
- Multi-Master Replication. Full and Fast Recoverability
- 100% Read Concurrency, Near Full Write Concurrency
- Online Backups, Point-in-Time Recovery, Replication, Warm Standby
- Dynamic and Automatic Indexing – All committed triples are always indexed (7 indices)
- Advanced Text Indexing – Text indexing per predicate
- Two-Phase Commit – SOLR and MongoDB Integration
- SPIN support (SPARQL Inferencing Notation). The SPIN API allows you to define a function in terms of a SPARQL query and then call that function in other SPARQL queries. These SPIN functions can appear in FILTERs and can also be used to compute values in assignment and select expressions.
- All Clients based on REST Protocol – RDF4J, Java Jena, Python, C#, Clojure, Perl, Ruby, Scala, and Lisp clients
- Completely multi-processing based (SMP) – Automatic Resource Management for all processors and disks, and optimized memory use. See the performance tuning guide here, and server configuration guide here
- Column-based compression of indices – reduced paging, better performance
- Triple Level Security with Security Filters
- Cloud-Hosted AllegroGraph – Amazon EC2
- The AllegroGraph RDF server can be scripted using the JavaScript API
- JavaScript-based interface (JIG) for general graph traversal
- Soundex support – Allows Free text indexing based on phonetic pronunciation
- User-defined Indices – fully controllable by system administrator
- Client-Server GRUFF with Graphical Query Builder
- Plug-in Interface for Text Indexers (use SOLR/Lucene, Native AG Full Text Indexer, Japanese Tokenizer)
- Dedicated and Public Sessions – In dedicated sessions users can work with their own rule sets against the same database
- Visit our Learning Center
<!–
* AllegroGraph is 100 percent ACID, supporting Transactions: Commit, Rollback, and Checkpointing.
* Full and Fast Recoverability
* 100% Read Concurrency, Near Full Write Concurrency
* Online Backups, Point-in-Time Recovery, Replication, Warm Standby
* Dynamic and Automatic Indexing – All committed triples are always indexed (7 indices)
* Advanced Text Indexing – Text indexing per predicate
* SOLR and MongoDB Integration
* SPIN support (SPARQL Inferencing Notation). The SPIN API allows you to define a function in terms of a SPARQL query and then call that function in other SPARQL queries. These SPIN functions can appear in FILTERs and can also be used to compute values in assignment and select expressions.
* All Clients based on REST Protocol – RDF4J, Java Jena, Python, C#, Clojure, Perl, Ruby, Scala, and Lisp clients
* Completely multi-processing based (SMP) – Automatic Resource Management for all processors and disks, and optimized memory use. See the performance tuning guide here, and server configuration guide here
* Column-based compression of indices – reduced paging, better performance
* Triples Level Security with Security Filters
* Cloud-Hosted AllegroGraph – Amazon EC2
* The AllegroGraph RDF server can be scripted using the JavaScript API
* JavaScript-based interface (JIG) for general graph traversal
* Soundex support – Allows Free text indexing based on phonetic pronunciation
* User-defined Indices – fully controllable by system administrator
* Client-Server GRUFF with Graphical Query Builder
* Plug-in Interface for Text Indexers (use SOLR/Lucene, Native AG Full Text Indexer, Japanese Tokenizer)
* Dedicated and Public Sessions – In dedicated sessions users can work with their own rule sets against the same database
* Visit our Learning Center
–>
-
Key Benefits
Features Advantages Benefits RDF/RDFS/JSON-LD
W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) industries Standards Standards based graph data and schema exchange format for interoperability
Standards basis enables interoperability and easy data exchange while maintaining data structure. Proprietary graph solution like Neo4j can’t exchange data and retain intelligence - Allows applications to remain flexible and easily/incrementally adapted to new and rapidly changing business needs.
- Seamless interoperability with public – private data sources.
- Supports the needs of unstructured and structured data to allow applications to reflect real world data sources.
- No Vendor lock-in.
SPARQL
W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) industries Standards Standard query language – for building complex, semantic queries
Standards basis enables transportability, large network of people know SPARQL, easier paths of migration, greater integration to other data query methods. Proprietary graph solutions like Neo4j have immature, proprietary query forms. - Built for and optimized to support unstructured, semi-structured and structured data queries.
- Easily spans multiple, public and private data sources to enable new and unique business queries and analytics.
- Works well with unpredictable, unreliable and changing data sources.
- Excellent at answering questions when relationships have to be used to answer queries.
- No Vendor lock-in.
Hypergraph – Property Graph Permits
Hypergraph – Property Graph Permits greater flexibility, performance and accuracy than simple Property Graph models in representing complex, real-world data relationships.
More comprehensive data representation enables a broader range of queries that better match the real world, more complex, more efficient. Simple property graphs are a limited data representation - Enables better and more accurate representations of real world information that results in faster and more accurate results.
- Greater flexibility in the creation of applications.
- Faster, higher value query results that relate better to business issues.
- No Vendor lock-in.
Advanced Queries
- Geospatial
- Temporal
- Social Networking
Combined query with simultaneous geo-spatial, temporal, social network analytics.
Better represent the real world and to answer queries that are impossible with relational databases and difficult with Hadoop. Optimized for complex semantic queries. Enables the concept of Events that have: - Locations
- Timeframes
- Relationships of People
- Activities
Better represent the real world and to answer queries that are impossible with relational databases and difficult with Hadoop.
Linked Open Data
Standard for data linking and exchange
Standards basis enables interoperability with data sources inside and out of the enterprise. Proprietary graph solutions like Neo4j can’t link. Provides the ability to link to the data elements of 1,000s of publically published, extremely rich, topic specific semantic graph databases to enhance and enrich an existing graph database. Reasoning Ontologies
W3C Industry Standard
OWL/SKOS for reasoning and inferencing – provides organization and structure to represent the knowledge in and about the data and metadata.
Standards basis for ontologies enables shared, compatible integration of other and multiple ontologies. Proprietary graph solutions like Neo4j can’t take - Flexibility to leverage existing ontologies for agility, speed and reduced cost of application development.
- Creates new insight via existing information.
- Implicit and standards based interoperability simplifies development
- Enables a single, unified virtual view across multiple repositories with structured or semantic schemas.
- Eliminates need for point-to-point integration thereby reducing costs, speeding time to develop, reducing development risk.
- Establishes a common semantic meaning across disparate systems to allow federated queries.
Better represent the real world and to answer queries that are impossible with relational databases and difficult with Hadoop.
ACID Database model
Simple graph systems, and NoSQL systems do not adhere to the full transactional ACID model and data integrity. Mission critical applications require 100% transactional integrity, and recoverability from interruptions. By providing a full ACID compliant transactional database model, AG is resilient and can work in any enterprise class application. Rules and logic
Support industry standard Prolog
Powerful rules language enables advanced integration to support complex queries. Allows for advanced business rules to support complex decision support and to more accurately build predictive systems that reflect the real world. Magic Predicates
Predicates can be defined by computed variables based upon formulas or conditional logic
Complex data requires flexibility to perform complex queries. Allows for a better representation of real world subtilize in the processing of complex data for more accurate predictions. Flexible APIs
Java, Python, C#, Ruby, Perl, Lisp, Clojure/Scala
Provides open language access to handle custom development and integration needs Complex applications need access to the core AG engine to String support
Unlimited data element length to enable support of lengthy URLs/URIs.
Creates greater flexibility in designing systems, especially when federation of queries across multiple databases is needed. Without this feature, other systems are limited in reference to data. No limit to length of URI references so easier to build real world applications. Dereferenceable URI
Nodes in the graph database can be data or can point to data external to the core graph database in an enterprise or information located on the Web.
Creates greater flexibility in designing systems, especially when linking external data sources and federation of queries across multiple databases is needed. Without this feature, other systems are limited in reference to data. - Expands the reach of graph data to external data and sources which greatly increases the value and flexibility of solutions built on the platform.
- Leverages the entire Web as informational sources to be linked to by the graph database.
- Substantially enhancing the practical use and value of information.
Enterprise Platform
Very mature platform – Enterprise scale, ACID, commit, roll-back, checkpoint, replication, warm standby, triple level security model, SMP, Cloud enabled, auditing
Mission critical business applications require enterprise features for ongoing operations, high availability, security, scalability. - Analytics based upon graph databases have become mission critical to the daily business operations. Graph databases therefore, require enterprise class database features to be robust, reliable and for high availability.
Cloud and on-premise licensing
AllegroGraph can run locally, or can be run from the Amazon Web Services (AWS) scalable cloud
Flexibility to run AllegroGraph in the form that fits the business and technical needs. - On-premise allows clients with sensitive data to keep work completely behind their firewalls.
- AWS provides a fast and incrementally economical subscription pricing.
- AWS provides quick and easy scalability, so projects can ramp up on demand.
Predictive Analytics
Analyzing and predicting via highly complex data across multiple data bases
The combination of graph, semantics, rules/logic, inferencing, BBN, Geospatial/Temporal/SNA provide a uniquely powerful predictive analytics platform. - Predictive Analytics have become mission critical to the daily business operations. Semantic Graph databases can provide advanced analytics un-achievable with any other technology.
Event support
Support for events that combine geo-spatial, temporal, rules and machine learning
Can answer queries that are unanswerable with traditional graph, NoSQL and Relational DB technology Complex business problems require sophisticated ability to model the real world and real-time events. -
New Features
* Triple Attributes Enhancements. The Triple attributes facility, allows each triple to have associated attributes. These can be used for various purposes, such as access control.
* New AGTOOL – Updated and Optimize command-line utility combines most individual command-line programs into one.
** archive — see Backup and Restore
** materialize — see Materializer
** export — see Data Export
** load — see Data Loading
** recover — see Point-in-Time Recovery
** replicate — see Replication
** upgrade — see the agtool upgrade program in the Database Upgrading document.
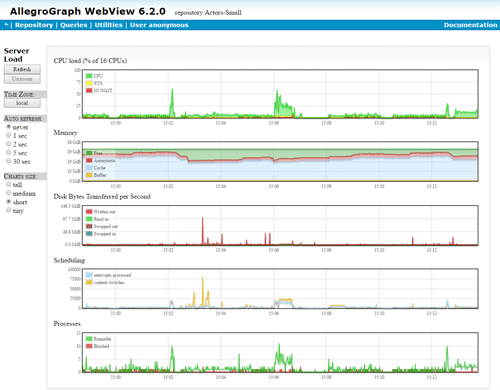
* New Server Performance Charts added to AGWebView. See screenshot below.
* Certification on Cloudera Enterprise
* Support for loading files from Hadoop Distributed File System; see Loading files from HDFS filesystems in Data Loading. Loading from HDFS file systems has been tested with the Cloudera Hadoop distribution.
* AllegroGraph Federation improvements – Improved and optimized communication between the main server and leaf nodes improves overall performance 2x for most users, and some operations by up to 50x. Federation is discussed in the AllegroGraph Introduction.
* Query Engine Optimizations:
** Improved SPARQL Processing Efficiency
** Improved Support for SPARQL Endpoints
** Improved Support for SPARQL Magic Properties
** More efficient use of temporary disk space
** Improved handling of very large result sets
* Storage Layer Operations:
** New Style2 Indices (optimizing point queries). See Style2Indices
** Reduced I/O of some data types
** Improved handling when out of disk space conditions exist
* Improved Auditing (see Auditing)
* Improved Online Backup and Restore (see Backup and Restore)
* Improved operations with freetext indices (see Full-text Indices)
* Python3 Client
* Updated RDF4J (2.7.11) and Jena (2.11.1), both clients that support Java 1.6.
Additional New Features
* Support for loading files from the Hadoop Distributed File System; see Loading files from HDFS filesystems in Data Loading
* New 3D and multi-dimensional geospatial functionality (see N-dimensional Geospatial)
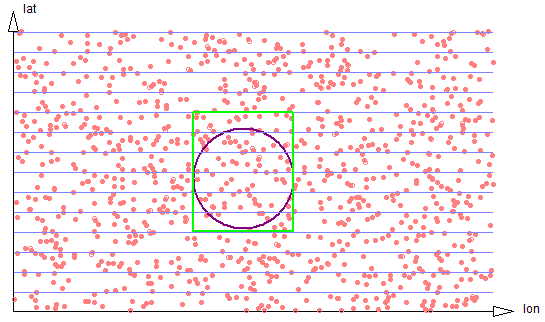
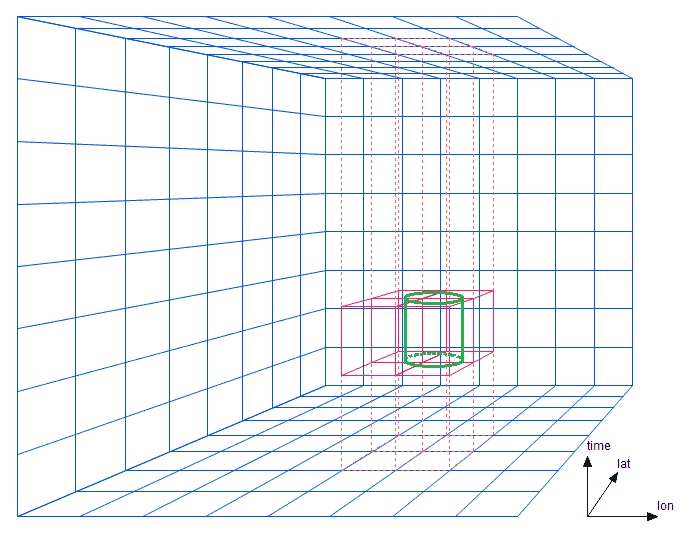
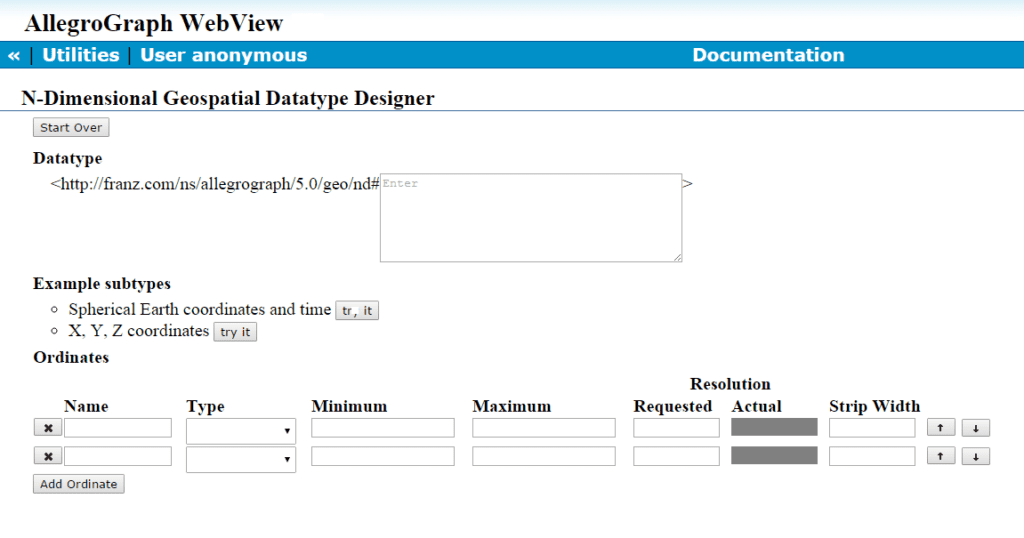
* Update to new RDF4J 2.7.x transactional semantics (see Javadocs (RDF4J and Jena))
* Update to new Apache Jena v2.6.x (see Javadocs (RDF4J and Jena))
* WebView query page improvements: display of execution time and abort options (see WebView)
* SPARQL v1.1 support for Geospatial, Temporal, and Social Network Analytics
* The server supports new optional specific transaction “begin”
* Improved support for encrypted client connections
* Query Engine Improvements
* Support for Top Braid Composer 4.5. See Top Braid Composer Plugin
* SPARQL Query Engine Enhancements
** Improved Query Optimizer
** SPARQL Performance Improvements
** Improved Query Memory Management
* Parallel Data Export
* Enhanced SPARQL “Magic Properties” or “Property Functions”
* Javascript API Updates
* Materialized Reasoner Improvements
* Query Plan Analyzer Improvements
* Enhanced Integration with MongoDB – Presentation: MongoDB meets the Semantic Web, and a recent Webcast on MongoGraph
* SOLR Interface for free text indexes, integrated with the SPARQL 1.1 query engine. View the webcast: Making Solr Search Smarter using RDF
The primary improvements to this latest AllegroGraph release are connectivity, third party integration and ingestion of data. There are many new features as well. Please refer to the release notes for a complete list of enhancements and improvements https://franz.com/agraph/support/documentation/current/release-notes.html .
-
High-performance Storage
AllegroGraph is designed for maximum loading speed and query speed. Loading of quads, through its highly optimized RDF/XML and N-Quads parsers, is best-of-breed, particularly with large files. The AllegroGraph product line has always pushed the performance envelope starting with version 1.0 in 2004, which was the first product to claim 1 billion triples loaded and indexed using standard x86 64-bit hardware.
AllegroGraph, a purpose built (not a modified RDBMS), NoSQL Graph Database continued to drive innovation in the marketplace with the 2008 SemTech conference example of 10 billion quads loaded on Amazon’s EC2 service. The new version 4 series continues to bring performance to the forefront of Franz’s Semantic Technologies as the industry’s first OLTP semantic web database. AllegroGraph’s ability to automatically manage all available hardware resources to maximize loading, indexing and query capabilities once again raises the bar for RDF storage performance. The following table displays examples of AllegroGraph’s performance in loading and indexing. Benchmark Results.
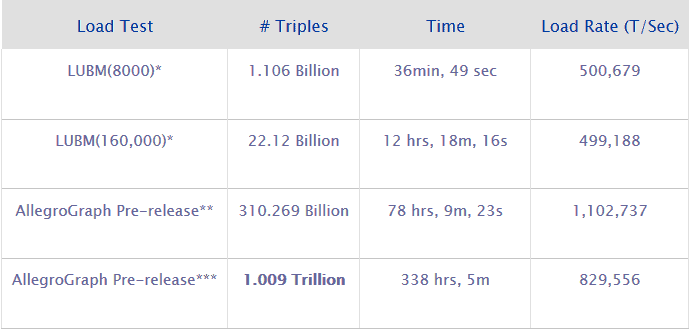
*32 core Intel E5520, 2.0 GHz, with 1 TB RAM, RedHat v6.1.
**64 core Intel x7560, 2.27 GHz, 2TB RAM, 22TB Disk, Redhat v6.1. LUBM-like data.
***240 core Intel x5650, 2.66GHz, 1.28TB RAM, 88TB Disk, Redhat v6.1. LUBM-like data.
-
Architecture
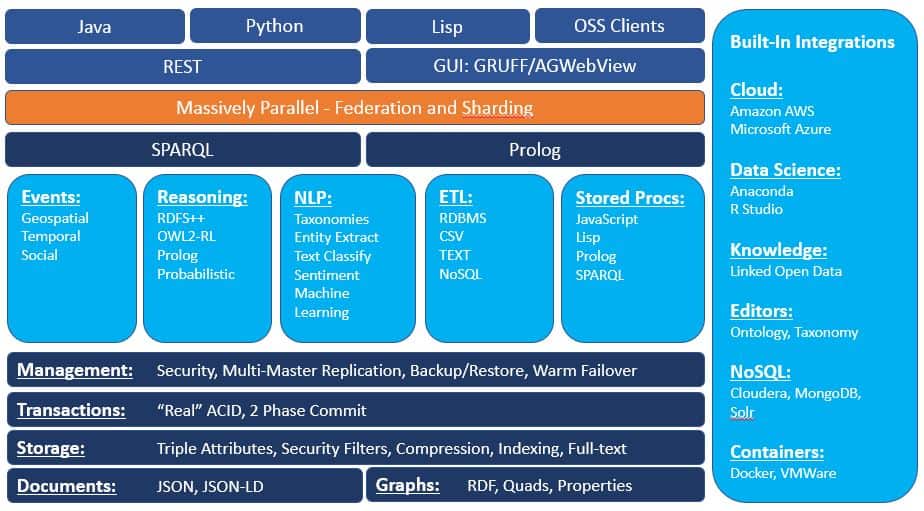
AllegroGraph provides a REST protocol architecture, essentially a superset of the RDF4J HTTP Client. Franz’s staff directly supports adapters for various languages, RDF4J Java, RDF4J Jena, Python using the RDF4J signatures, and Lisp. There are Open Source Adapters through community projects for C#, Ruby, Clojure, Scala, and Perl. Links to download here.
-
Powerful and Expressive Reasoning and Querying
AllegroGraph provides the broadest array of mechanisms to query and access knowledge in an RDF datastore:
RDFS++ Reasoning – Dynamic Materialization
Description logics or OWL-DL reasoners are good at handling complex ontologies. They tend to be complete (give all the possible answers to a query) but can be totally unpredictable with respect to execution time when the number of triples increases beyond millions. AllegroGraph offers a very fast and practical RDFS++ reasoner.We support all the RDF and RDFS predicates and some in full OWL. The supported predicates are RDF:type, RDFS:subClassOf, range, domain, subProperty.
OWL:sameAs inverseOf, TransitiveProperty, hasValue, someValuesFrom, allValuesFrom, one of, equivalentClass, restriction, onProperty, intersectionOf.
AllegroGraph’s RDFS++ engine dynamically maintains the ontological entailments required for reasoning: it has no explicit materialization phase. Materialization is the pre-computation and storage of inferred triples so that future queries run more efficiently. The central problem with materialization is its maintenance: changes to the triple-store’s ontology or facts usually change the set of inferred triples. In static materialization, any change in the store requires complete re-processing before new queries can run. AllegroGraph’s Dynamic Materialization simplifies store maintenance and reduces the time required between data changes and querying.
OWL2 RL Materialized Reasoner
AllegroGraph’s OWL2 RL materializer uses a set of inference rules to generate new triples and adds them to the database. OWL 2 RL is the subset of OWL 2 that is designed to support rule based reasoners. OWL 2 RL contains a large number of rules for generating triples and some rules for verifying that the triple store is consistent with respect to the OWL 2 RL ontology. The OWL2 RL materializer is best when OWL 2 RL inference is required or the store is relatively static.SPARQL Queries on Named Graphs
SPARQL, the W3C standard RDF query language, returns RDF, XML and other formats in responses to queries. AllegroGraph’s SPARQL, one of the W3C’s “interoperable implementations”, includes a query optimizer, and has full support for named graphs. It can be used with the RDFS++ reasoning turned on (i.e., query over real and inferred triples). SPARQL can be used with every available AllegroGraph interface mentioned in the previous section.Prolog
AllegroGraph’s RDF Prolog provides concise, powerful, industry-standard, domain-specific reasoning to build high-level concepts (that require complex rules or numerical processing) on top of RDF data. AllegroGraph Prolog is an option because many use cases are difficult (or very cumbersome) to model with only RDF/RDFS and OWL. Prolog can also be used on top of the RDFS++ reasoner as a rule based system.Low-level APIs Allow fast, ‘close-to-the-metal’ access to triples by subject, predicate, and object.
-
Geo-spatial, Temporal and Social Network Analysis
Geospatial and Temporal Reasoning
AllegroGraph stores geospatial and temporal data types as native data structures. Combined with its indexing and range query mechanisms, AllegroGraph lets you perform geospatial and temporal reasoning efficiently.Social Networking Analysis
AllegroGraph includes an SNA library that treats a triple-store as a graph of relations, with functions for measuring importance and centrality as well as several families of search functions. Example algorithms are nodal-degree, nodal-neighbors, ego-group, graph-density, actor-degree-centrality, group-degree-centrality, actor-closeness-centrality, group-closeness-centrality, actor betweenness-centrality, group-betweenness-centrality, page-rank-centrality, and cliques. Geospatial and temporal primitives combined with SNA functions form an Activity Recognition framework for flexibly analyzing networks and events in large volumes of structured and unstructured data. -
Enterprise Features
Unlike traditional relational databases or more recently developed NoSQL databases, Franz’s product AllegroGraph employs a combination of semantic and graph technologies that process data with contextual and conceptual intelligence. AllegroGraph is able to run queries of unprecedented complexity to support predictive analytics that help companies make better, real-time decisions.
-
Other powerful features
Native Data Types and Efficient Range Queries
AllegroGraph stores a wide range of data types directly in its low level triple representation. This allows for very efficient range queries and significant reduction in triple-store data size. With other triple-stores that only store strings, the only way to do a range query is to go through all the values for a particular predicate. This works well if everything fits in memory; but if the predicate has millions of triples, it will need costly machines with huge amounts of RAM. AllegroGraph supports most XML Schema types (native numeric types, dates, times, longitudes, latitudes, durations and telephone numbers).Free-text Indexing
AllegroGraph supports free-text indexing on the objects of triples whose predicates have been registered for indexing. Once indexed, triples can be found using a simple but robust query language. Free-text indexing support includes functions to register predicates and see which predicates are registered. Support for Solr was added in AllegroGraph version 4.5Named Graphs for Weights, Trust Factors, Provenance
AllegroGraph actually stores quints. A triple in AllegroGraph contains 5 slots, the first three being subject (s), predicate (p), and object (o). The remaining two are a named-graph slot (g) and a unique id assigned by AllegroGraph. The id slot is used for internal administrative purposes, but can also be referred to by other triples directly.The W3C proposal is to use the ‘named-graph’ slot for clustering triples. So for example, you load a file with triples into AllegroGraph and you use the filename as the named-graph. This way, if there are changes to the triple file, you just update those triples in the named graph that came from the original file. However, with AllegroGraph, you can also put other attributes such as weights, trust factors, times, latitudes, longitudes, etc, into the named graph slot.Direct Reification
AllegroGraph allows triple-ids to be the subject or object of another triple. This is beyond the scope of pure RDF. The advantage of this approach is that you can reduce the total number of triples in the store to a more manageable size, and, even more importantly, dramatically reduce query time because a single query can retrieve more data.Automatic Resource Management
The AllegroGraph architecture is designed to maximize hardware resources for all data management procedures (Loading, Indexing, Query, etc.). The hardware utilization can be managed through the AllegroGraph configuration file as necessary.Dynamic and Automatic Indexing
Triple-indices are user configurable, or index management can be taken care of entirely by AllegroGraph. By default, all committed triples are always indexed (default: 7 indices). AllegroGraph now supports any index combination of S, P, O, G. The default indices are:* S, P, O, G, I – Subject, Predicate, Object, Named Graph, ID
* P, O, S, G, I
* O, S, P, G, I
* G, S, P, O, I
* G, P, O, S, I
* G, O, S, P, I
* I
-
Compatible Semantic Technologies
Pool Party
Pool Party is a world-class semantic technology suite that offers sharply focused solutions to your knowledge organization and content business. Pool Party is the most complete semantic middleware on the global market. Use it to enrich your information with valuable metadata. Let it link your business and content assets automatically. Pool PartyTopBraid Composer
TopBraid Composer, developed by TopQuadrant, Inc., is an enterprise-class modeling and application development environment It provides comprehensive support for modeling ontologies and data, connecting data sources, designing queries, rules and semantic data processing chains, and developing Semantic Web applications. For details see TopBraid ComposerAGWebview
AGWebview, developed by Franz, Inc., is an interface for exploring, querying, and managing AllegroGraph triple stores through a web browser. For details see AGWebviewGruff
Gruff is an RDF browser that displays visual graphs and has an interface to build SPARQL or Prolog queries as visual graphs. Gruff can also display tables of all properties of selected resources or generate tables with SPARQL queries, and resources in the tables can be added to the visual graph. For details see GruffDATAmaestro
Data mining has increasingly played a key role in the enterprise decision process because of today’s competitive necessity to respond to changing market conditions quickly and correctly, leveraging the enormous operating data now available for such process. DATAmaestro, developed by PEPITe S.A. brings unique capabilities to meet today’s data mining needs. For details see DATAmaestroCogito
The COGITO platform by Expert System S.p.A., conceived to bring intelligence to the search, extraction and classification of unstructured information for internal management purposes and for monitoring and analyzing external sources, such as the Internet. For details see CogitoSentient Suite
The Sentient Suite, developed by Melissa Informatics (formerly IO Informatics Inc.), integrates heterogeneous data to solve knowledge and project management problems for the Life Sciences industry. For details see Sentient SuiteTalend Open Studio
Talend Open Studio is an open source, Eclipse-based environment offering the broadest connectivity to all source and target systems to support all types of data integration, data migration and data synchronization operations. For details see Talend
Semaphore
Semaphore is an Enterprise Content Intelligence Platform built from four core and inter-connected modules: an Ontology Manager, Classification and Text Mining, a Semantic Enhancement Server, and a Search Application Framework. Semaphore: Automatically, accurately and consistently applies metadata and classification, Improves find-ability by being ontology-driven, Provides a better search and navigation experience, and Enables effective data disposition, data loss prevention, records retention and eDiscovery. For more details see SmartLogic -
System Requirements
The AllegroGraph Database Server runs natively on Linux x86-64 bit. To run AllegroGraph on other operating systems (i.e. Windows, Mac) we suggest you set up a Linux Virtual Machine or EC2. We provide a Virtual Machine and EC2 AMIs to help facilitate installation. Clients to an AllegroGraph server may be any OS and either 32-bit or 64-bit. franz.com/agraph/downloads/clients?ui=new

The Virtual Machine Appliance will let you run the AllegroGraph Linux version on a Windows or Mac operating system. Performance will be slower than running natively, so we encourage you to install AllegroGraph natively for performance evaluation.
Installation details for the Virtual Machine Appliance.
-
Benchmarks
-
Documentation
For more info, send email to [email protected] or call (510) 452-2000, Option 3-Sales and Marketing

